The function and working principle of circuit breaker
A circuit breaker is a switching device that can close, carry and break the current under normal loop conditions, and can close, carry and break the current under abnormal loop conditions (including short-circuit conditions) within a specified time. Circuit breakers can be used to distribute electrical energy, start asynchronous motors infrequently, and protect power lines and motors. They can automatically cut off the circuit when they have serious overload, short circuit, or undervoltage faults. Its function is equivalent to a fuse switch Combination with overheating and underheating relays. Moreover, it is generally not necessary to change parts after breaking the fault current. At present, it has been widely used.
The circuit breaker is generally composed of a contact system, an arc extinguishing system, an operating mechanism, a trip unit, and a housing. Circuit breakers are divided into miniature circuit breakers, molded case circuit breakers and frame type circuit breakers according to their structure.
The role of circuit breakers
Cut off and turn on the load circuit, and cut off the faulty circuit to prevent the accident from expanding and ensure safe operation. The high-voltage circuit breaker needs to break the 1500V, current 1500-2000A arc, these arcs can be stretched to 2m and still continue to burn and not extinguish. Therefore, arc extinguishing is a problem that must be solved by high-voltage circuit breakers.
Low-voltage circuit breakers are also called automatic air switches, which can be used to connect and disconnect load circuits, and can also be used to control motors that start infrequently. Its function is equivalent to the sum of part or all of electrical appliances such as knife switch, overcurrent relay, voltage loss relay, thermal relay and leakage protector. It is an important protective electrical appliance in low-voltage power distribution network.
Low-voltage circuit breakers have a variety of protection functions (overload, short circuit, undervoltage protection, etc.), adjustable action value, high breaking capacity, convenient operation, and safety, so they are currently widely used. Structure and working principle The low-voltage circuit breaker is composed of operating mechanism, contacts, protection devices (various trip units), arc extinguishing system, etc.
Working principle of circuit breaker
When a short circuit occurs, the magnetic field generated by a large current (generally 10 to 12 times) overcomes the reaction force spring, the trip unit pulls the operating mechanism, and the switch instantaneously trips.
When overloaded, the current becomes larger, the heat generation increases, and the bimetal deforms to a certain extent to push the mechanism to move (the larger the current, the shorter the action time).
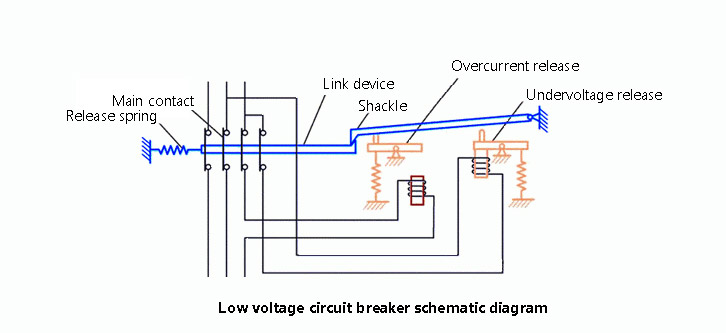
The main contacts of low-voltage circuit breakers are manually operated or electrically closed. After the main contact is closed, the free trip mechanism locks the main contact in the closed position. The coil of the overcurrent release and the thermal element of the thermal release are connected in series with the main circuit, and the coil of the undervoltage release is connected in parallel with the power supply. When the circuit is short-circuited or severely overloaded, the armature of the overcurrent release pulls in, causing the free tripping mechanism to act, and the main contact disconnects the main circuit. When the circuit is overloaded, the heating element of the thermal trip unit will bend the bimetal and push the free trip mechanism to move. When the circuit is undervoltage, the armature of the undervoltage release is released. It also makes the free trip mechanism act. The shunt release is used for remote control. During normal operation, its coil is de-energized. When distance control is required, press the start button to energize the coil, and the armature drives the free trip mechanism to move the main contact. Click disconnect.
Now there are electronic types, which use transformers to collect the currents of each phase and compare them with the set values. When the current is abnormal, the microprocessor sends out a signal to make the electronic trip unit drive the operating mechanism.
Parameters of circuit breaker
Rated working voltage (Ue): This is the voltage at which the circuit breaker works under normal (uninterrupted) conditions.
Rated current (In): The maximum current value that a circuit breaker equipped with a special overcurrent trip relay can withstand indefinitely under the ambient temperature specified by the manufacturer, and will not exceed the temperature limit specified by the current-bearing component.
Short-circuit relay trip current setting value (Im): The short-circuit trip relay (instantaneous or short delay) is used to quickly trip the circuit breaker when a high fault current value occurs, and its trip limit Im.
Rated short-circuit breaking capacity (Icu or Icn): The rated short-circuit breaking current of a circuit breaker is the highest (expected) current value that the circuit breaker can break without being damaged. The current value provided in the standard is the root mean square value of the AC component of the fault current. When calculating the standard value, the DC transient component (always appearing in the worst-case short circuit) is assumed to be zero. Industrial circuit breaker ratings (Icu) and household circuit breaker ratings (Icn) are usually given in the form of kA rms.
Short-circuit breaking capacity (Ics): The rated breaking capacity of a circuit breaker is divided into two types: the rated ultimate short-circuit breaking capacity and the rated operating short-circuit breaking capacity.