Common faults of circuit breaker control circuit
Fast and effective handling of control loop faults is an essential skill for relay protection personnel. However, because the secondary control loop faults are not intuitive, there are many secondary cables, and the loops are complicated, the fault point is unclear, and the search is like falling into the fog. Therefore, how to quickly and accurately find, handle and prevent secondary circuit faults is an important issue to improve the safe and stable operation of power grids and equipment.
1. The control circuit of the circuit breaker
1.1 Principle of control circuit disconnection
Control loop failure is generally manifested as a control loop disconnection alarm. The control loop disconnection alarm signal loop uses the series connection of the closing position relay HWJ normally closed contact and the tripping position relay TWJ normally closed contact inside the protection device. When the circuit breaker is in the closing position, the closing position relay is excited; when the circuit breaker is in the trip position, the trip position relay is excited. When the control loop fails and causes the closing position relay and the trip position relay to lose magnetism at the same time, the HWJ and TWJ normally closed contacts are closed at the same time, and the protection device will issue a "control circuit disconnection" alarm signal.
1.2 Common monitoring methods
There are two common methods for monitoring the integrity of the control loop: direct monitoring using simple and intuitive traffic light loops; indirect monitoring of the central signal using the normal closed contacts of the trip and closing position relays in series.
2. Types of control loop failures
There are many reasons for the disconnection of the control circuit. The main reasons are as follows:
(1) The control power air switch trips, malfunctions or the control power fuse is blown;
(2) The auxiliary contact of the circuit breaker is poorly contacted or damaged;
(3) The opening and closing coils are burnt or disconnected;
(4) The energy storage circuit is faulty, the energy storage motor or the energy storage travel switch is damaged, and the energy storage contact is poorly contacted;
(5) The electromagnetic closing coil of the electromagnetic operating mechanism is burned.
3. Troubleshooting method of control loop
Although the basic control logic is the same, the implementation methods of the secondary circuit are different. To quickly deal with the disconnection fault of the control circuit, it is necessary to have a clear understanding of the backbone of the circuit breaker control circuit and combine the different fault phenomena on the spot to form a basic judgment. The control circuit diagram of the circuit breaker mechanism is shown in Figure 1.
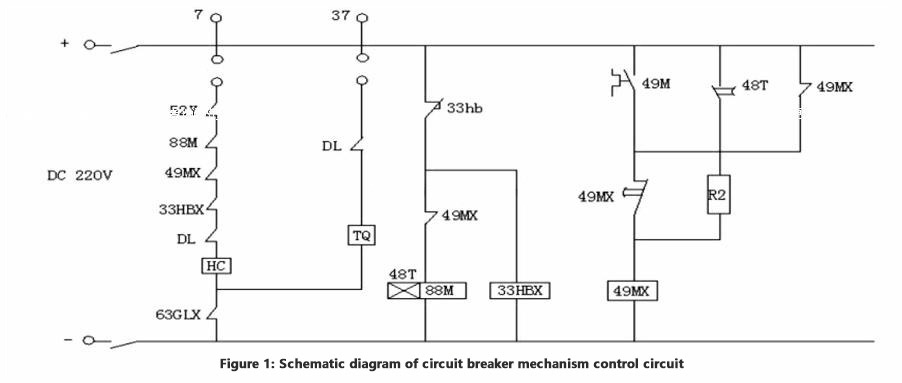
Common control loop disconnection faults and treatment methods are summarized as follows.
(1) Ask the on-site staff about the relevant site conditions, that is, the primary and secondary operations, circuit breakers, and protection actions; investigate the situation in a targeted manner according to the site conditions.
(2) There is a burning smell at the scene, which can be basically judged as the following three categories: the opening and closing coils are burned; the electromagnetic closing coil of the electromagnetic operating mechanism is burned; the energy storage motor of the spring operating mechanism is burned.
- If the opening and closing coils and electromagnetic closing coils are burnt, replace them with new ones. Causes of coil burnout include: mechanical failure of opening and closing, failure of reliable switching of auxiliary contacts, poor coil quality or aging. Because the current microcomputer protection control circuits all have opening and closing self-holding circuits, if the circuit breaker does not open (close) for some reason, or the auxiliary contact of the circuit breaker does not switch in place after the trip (close), Then the trip (closing) circuit will always be in a live hold state, and the opening and closing coils and electromagnetic closing coils will be burned. Therefore, when replacing the new coil, you should also check the cause of the coil burnout, and eliminate the defect completely.
- The energy storage motor needs to be replaced with a new motor if it burns out. There are three main reasons for the energy storage motor burnout: the relay and its auxiliary contacts of the energy storage motor are damaged or the energy storage travel switch and its auxiliary contacts are faulty or stored. The motor power is small. For example, when the energy storage power supply cannot be cut off due to the failure of the limit switch and its auxiliary contact in the energy storage circuit, or the relay or its auxiliary contact 49MX in the energy storage circuit is damaged as shown in the figure, the energy storage motor will be burned. Therefore, after replacing the energy storage motor, you should also find out the reason that caused the motor to burn out, otherwise the energy storage motor will burn out again.
(3) Use a multimeter to measure the upper and lower pile heads of the control power supply to see if the DC voltage to ground is normal and whether there is a short circuit at the lower pile head: if the lower pile head is not live, consider the air switch trip; if the upper and lower pile head voltages are equal Normal, combined with the red and green light states to preliminarily judge the circuit where the fault is located:
- The circuit breaker is closed and the red light is off: open the circuit. If it can be opened, only the red light indicates the circuit failure or the bulb is broken. There are two situations for unsuccessful switching: First, use a multimeter to measure the loop 37 with negative power, indicating that the fault point is between the positive power of the control power supply and the tripping loop of the measured circuit 37 terminal, and the control power supply needs to be positively charged to the measured loop. Check the trip circuits among the 37 terminals one by one; secondly, use a multimeter to measure that the circuit 37 is positively charged, indicating that the fault point is between the terminal block circuit 37 and the trip circuit of the circuit breaker mechanism that controls the negative power of the power supply, and the terminal block circuit 37 to control Check the loops between the negative power supply one by one.
- The circuit breaker is in position, and the green light is not on: the closing operation is carried out. If the closing can be carried out, only the green light indicates circuit failure or bulb failure. If the closing is unsuccessful, there are also two situations: First, use a multimeter to measure the circuit 7 with negative power, indicating that the fault point is between the positive power of the control power supply and the closing circuit of the terminal 7 of the tested circuit. Same as the closing position, the first half of the circuit needs to be checked one by one; second, use a multimeter to measure the circuit 7 with positive power, indicating the fault The point is between the terminal block circuit 7 and the closing circuit of the circuit breaker mechanism that controls the negative power of the power supply. Like the closing position, the latter half of the circuit needs to be checked one by one.
4. Prevention of control loop failure
In combination, the reasons for the failure of the control loop are nothing more than equipment quality problems, engineering construction quality problems, regular inspection and maintenance problems, and operating environment problems.
First of all, according to the comprehensive consideration of the operating environment of the equipment, try to use equipment and accessories of good quality from regular manufacturers; secondly, strictly pay attention to the construction and acceptance links, and strive to achieve zero defects in equipment and circuits into operation; finally, the equipment is regularly inspected and maintained. In addition to the logic verification of the protective device and the secondary circuit in the acceptance and debugging of new equipment, the focus of later periodical inspection and maintenance should be placed on the inspection of the secondary circuit, especially the first periodical inspection of the new equipment after a full year of operation. Because the stress of the new screws of the secondary circuit disappeared at this time, many screws began to loosen, or the initial appearance of the influence of the operating environment on the insulation of the secondary circuit and other problems began to be gradually exposed, so seize this critical time node to conduct timely maintenance and repair. To a large extent, it reduces the pressure of later maintenance and elimination.
The integrity of the control loop directly affects the safe and stable operation of the circuit breaker. We are proficient in how to quickly and effectively handle the control loop failure to prevent the circuit breaker from skipping tripping in the event of a failure. This will expand the scope of the accident and ensure the safe and stable operation of the power grid and equipment. And ensuring the reliability of power supply is of great significance.